
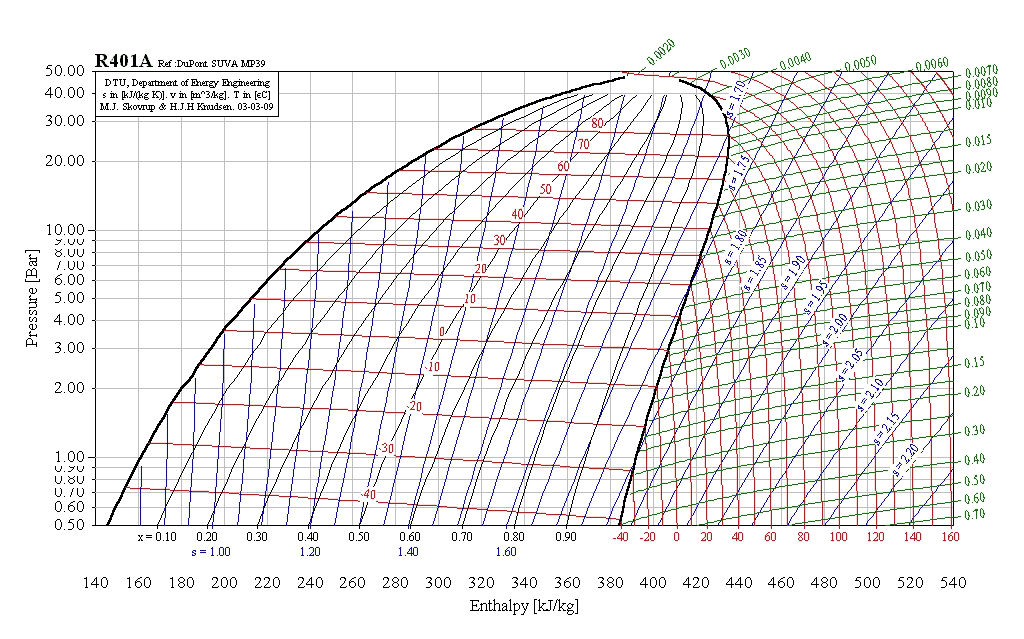
The diagram for the total turbine, as well as its constituent components, flows, and energy interactions are shown in the diagram below:įor the each section of the turbine, the simplified conservation laws for these steady-state adiabatic devices are: Given the more complicated flow regime of this intermediate-bleed turbine, it’s worth evaluating it based on first principles and deriving useful relationships. Properties at State 5 (Superheated Vapor): The only other state in the cycle for which all properties are easily found is state 5. We therefore need to determine the properties at state 6a to obtain the properties at state 3. In which ℎ 3 is found to be the mass-weighted average of the enthalpies of the two contributing streams. Which, when combined with conservation of mass yields

Note: The open feedwater heater is an adiabatic mixing chamber involving no work, where two streams of different, but related, mass flow rate enter, and the sum of their contributions exit. Properties at State 2a (Compressed Liquid): Process 1 → 2a (Irreversible compression in a pump): Note: the subscript “Y” is there to remind us that this work input is per kilogram of liquid flowing through the pump, but the flow rate is a fraction of the total amount of steam flowing through the HP side of the plant and will need to be multiplied by “Y” during the overall work & heat analysis of the plant. Process 1 → 2s (Isentropic compression in a pump): Properties at State 1 (Saturated Liquid): Power plant operating on Rankine Cycle with given properties and diagram.ĭetermine properties at important stages in the cycle: Since the streams are being split, we’ll need to keep track of the relative mass flow fractions with regard to turbine and pump work as well as condenser heat rejection and, if there’s boiler reheat, the mass fraction of steam being reheated.ĮXAMPLE 1 – REGENERATIVE RANKINE CYCLE WITH OPEN FEEDWATER HEATING AND ISENTROPIC INEFFICIENCIES. If you compare the pictures in these lecture notes to the ones in the book, you’ll notice this difference. The book uses a slightly different convention than I do I specify the fraction of steam that’s allowed to fully expand and condense as “Y” and the fraction of bled steam as “(1-Y)”. The flow of H 2O through the plant is being split, with some partially-expanded steam being sent laterally back to the pre-boiler side to heat the feedwater and the rest being allowed to fully expand through the turbines and subsequently condense in the condenser prior to being pumped, mixed with the bled steam, and then sent to the boiler. Partially-expanded steam destined for the FWH is bled from the turbine(s) at some intermediate pressure. The higher the average temperature of steam is in the boiler, the more efficient the cycle will be. The purpose of a feedwater heater is to preheat the feedwater prior to entering the boiler, which reduces the amount of fuel that must be expended to increase the temperature of the feedwater to the boiler outlet temperature. Closed feedwater heaters are heat exchangers through which both streams flow but do not mix, therefore they can each enter at a different pressure relative to each other heat exchange is less effective for closed feedwater heaters. An open feedwater heater accepts both streams and mixes them and exhibits excellent heat exchange, but both streams must enter at the same pressure each open feedwater heater in a steam plant must have a dedicated pump associated with it.
#Enthalpy of feed water calculator how to#
Steady Flow Vapor Power Cycle – Rankine Cycle w/ Open Feedwater Heating - Class 13Īt the completion of the lecture, students should:ġ) Understand how to analyze the Rankine Cycle when an open feedwater heater is installed to extract partially-expanded steam from the turbine.įeedwater Heater: A heat-exchanging device into which feedwater is pumped and partially-expanded steam flows. Thermodynamics Data, Equations, Charts, Equations and Calculators
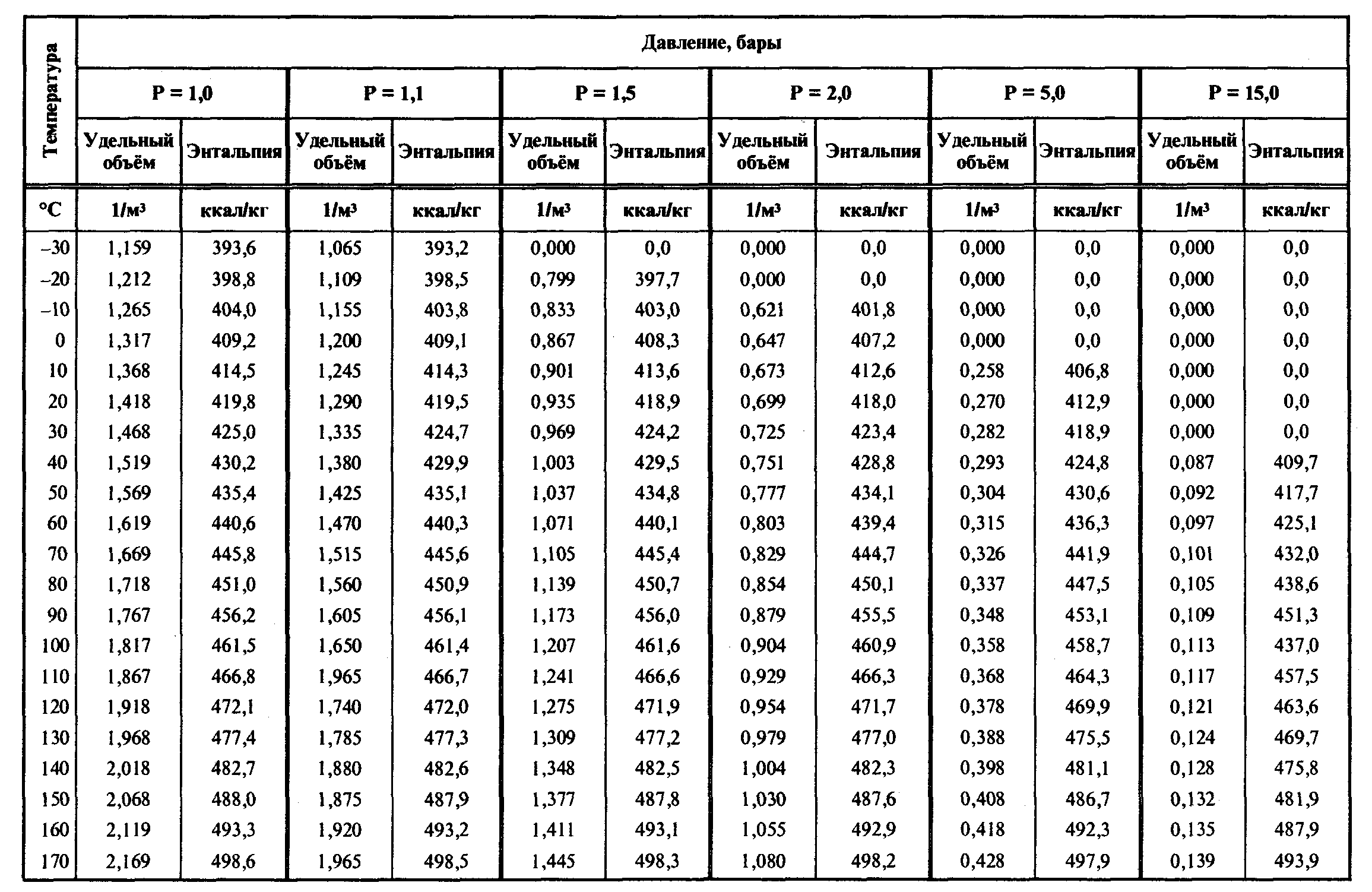
Related Resources: thermodynamics Steady Flow Vapor Power Cycle – Rankine Cycle w/ Open Feedwater Heating - Class 13


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
